Scenario Overview:
Chimp Corp has recently completed the acquisition of a competitor, Bananas Inc. As part of the core infrastructure architecture team, you have been brought in to design and implement Exchange 2013 as part of a large Enterprise systems refresh. The Project Charter has been signed off by senior stakeholders with the objective of upgrading the existing messaging environment from Exchange 2003 SP2 to Exchange 2013. Senior Management has expressed a desire to migrate the messaging environment to the cloud in order to take advantage of cost benefits, however the compliance department has mandated that specific components of the messaging environment must stay on-premises in order to meet regulatory requirements.
Management has decided to deploy a Hybrid Exchange 2013 environment in a new Active Directory Forest that is Federated to an Exchange Online organization. The on-premise environment will host approximately 60% of the Organization’s mailboxes and the remaining 40% of the Organization’s mailboxes are considered to be non-sensitive and the compliance department has approved their migration onto the cloud. This scenario represents the path of least resistance, as Microsoft Exchange 2013 does not support direct upgrade path from Exchange 2003 to Exchange 2013 and due to the considerable size of the corporate messaging environment (15,000 Mailboxes), a swing migration to Exchange 2007/2010 and then to Exchange 2013 was considered to be impractical.
Existing Environment:
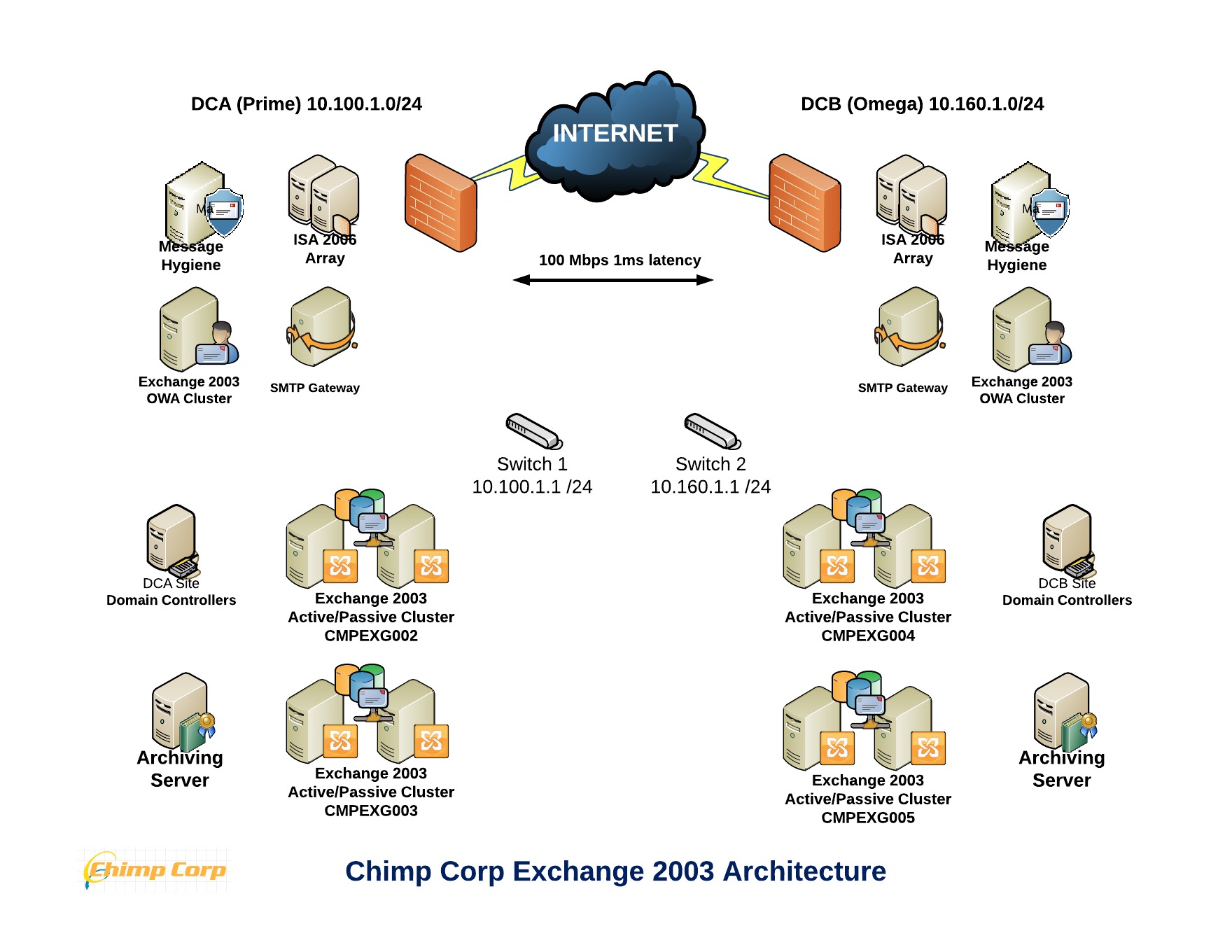
The messaging environment features Exchange 2003 SP2 with Active Directory 2008, featuring four Clustered Exchange Mailbox Servers implemented across two datacenters with dedicated Network Load Balanced Exchange Front End Servers in each location. Third-party SMTP Message Hygiene appliances were configured in each site to provide Spam Filtering and Anti Virus Scanning and in addition, a number of applications were configured to relay SMTP messages via one of the SMTP appliances. A third-party Archiving tool was deployed across both sites and client access was provisioned primarily via Outlook RPC, OWA; Blackberry Enterprise Servers and Microsoft ActiveSync.
Requirements:
The following solution requirements were distilled from theRequest for Proposal (RFP) document. The solution must:
- Conform to Microsoft Best Practices
- Accommodate 99.99% high availability standards
- Adhere to Disaster Recovery, High Availability and Business Continuity standards
- Provide a fully redundant and load balanced design
- Accommodate 9,000 Mailboxes across 2 datacenters
- Accommodate 6,000 Mailboxes on an Exchange Online organization
- Average Mailbox Size 1 GB
- Anticipated Storage Growth per year of 20%
- Store Archived Emails for 7 years
- Adhere to Retention, Legal Hold and eDiscovery requirements
- Perform Email Archiving whenever a mailbox reaches 1GB or whenever messages are 1 year old.
- Network Access Bandwidth: 1 Gbps
- Storage Access: Minimum bonded Gigabit Connections or Fibre Channel
- Client Access: Outlook 2007 and later, Internet Explorer, Safari and Firefox using OWA, PDA access from RIM Blackberries, IP Phones and Microsoft Windows Mobile 6 and later.
Proposed Solution:
Based on stipulated requirements in the RFP, the Proposed Solution must include a number of components including the following:
- Methodology used to implement Exchange 2013 and related architectural components
- Related hardware and software builds
- Related costs of implementing the solution
- Annual cost of ownership
- A high level project plan detailing the responsibilities of various stakeholders
The final solution proposed an implementation of Exchange 2013 configured as a Hybrid environment. The Exchange 2013 environment would feature the following benefits:
- Scalability and flexibility of moving users to the cloud
- Virtualization of on-premises Exchange environment
- Migration of Archives to Exchange Online Archiving
- Deployment of High Availability using native Microsoft technologies
- Unified Management via Microsoft Exchange Administration Center
- Systems Management via Microsoft System Center Configuration Manager (SCCM) 2012
Solution Components:
The solution featured a high-level design that was broken into the following components:
- Exchange Server
- Infrastructure Services
- Email Archiving
- Storage Design
- Backup and Recovery
- Systems Management
- Client Access
Conclusion:
Successive sections in this series will provide you with the various design components of the final solution, as well as related Project Implementation plans.
For Part 2: High-level Architectural Design Document, click here.
Excellent post. I used to be checking continuously this weblog and I am impressed!
Very helpful info specifically the final section 🙂 I care for such info much.
I used to be looking for this particular info for a long time.
Thank you and good luck.
looks like a huge project..
can you make a small project with less requirements and less resources..?
kindly post it if you have one.. thanks man.. its a real stuff..