For another installment of my list of most influential AI papers, here’s where the rubber hit the road, folks. Prior to distillation, running custom AI models was a costly and resource intensive process limited to those with deep pockets and access to large GPU clusters. This paper changed everything…
Paper’s name: DistilBERT, a distilled version of BERT: smaller, faster, cheaper and lighter (Oct 2019)
 Where are the lead Authors now?
Where are the lead Authors now?
Victor Sanh, Cofounder (Stealth Startup)
Lysandre Debut, Chief Open Source Officer (COSO), Huggingface
Julien Chaumond, Co-founder CTO, Huggingface
Thomas Wolf, Co-founder, Chief Science Officer, Huggingface
The Problem It Solved
At the time of writing, researchers had demonstrated that transfer learning techniques (such as pre-training) to train large language models could achieve significant improvements in performance. The leading research indicated that breakthrough performance could be achieved by training even larger models.
But training models with hundreds of millions of parameters and beyond required significant resources. This made it less accessible to organizations with budget constraints for training or inference; and also hindered application of these models for real-time use on a broad range of devices.
What’s It About?
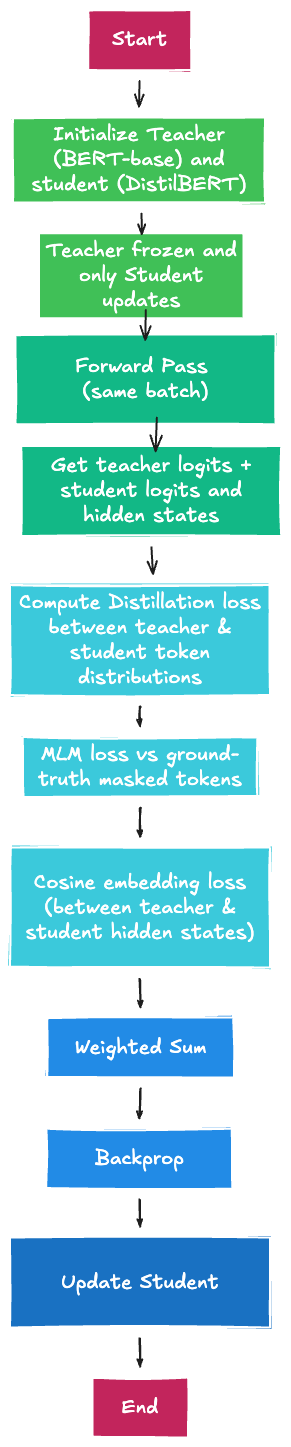
The authors adopted *knowledge distillation*, a compression technique in which a small model (known as a student) is pre-trained to reproduce the behavior of a much larger model (called the teacher), which could then be fine tuned on many downstream tasks. The authors demonstrated how their model DilstilBERT, built using this technique, was smaller than Google’s popular BERT model by 40%, while retaining 97% of language understanding capabilities and being 60% faster. Additionally, the authors tested DistilBERT on an iPhone 7 plus, performing 71% faster than the larger BERTbase, while consuming only 207MB on disk.
Why It Matters
– The authors proved that distillation on a general training set of tasks resulted in a model with a much smaller footprint with minimal loss in fidelity, while retaining significant improvements in performance.
– In terms of costs, the authors used a cluster of 8 x NVIDIA V100 GPUs running for 90 hours. In contrast, researchers at Facebook AI had developed a state of the art model RoBERTa, a just one year prior, by training on a cluster 128 times larger (1024 V100 GPUs for approximately one day).
– In terms of footprint, the authors demonstrated that a distilled model could run on edge devices like mobile phones.
Key Takeaways
– This paper helped popularize model distillation, paving the way for much smaller model footprints, local and even homegrown special-purpose LLMs designed for specific industry use cases.
– The race is on for edge compute AI. Up and down the value chain, with hardware manufacturers like Samsung, Huawei, Qualcomm (Snapdragon), Apple (Silicon), Mediatek and Google delivering technology stacks optimized for Edge AI.
So What?
– Imagine a future with ubiquitous LLMs, literally millions of AI models running on connected devices, equipment and infrastructure, trained with hyper-specific context to cater to individual needs.
– Huggingface’s contribution was to make knowledge distillation highly accessible and practical for a wide audience of developers and researchers. Their framework, the Hugging Face transformers library and associated tools incorporate knowledge distillation into their training pipelines, providing a simple, coding-free way to perform distillation experiments and share results. Today there are over 1M public model listings on Huggingface accessible to the public!
Link to full paper: Arxiv