Yet another installment of influential research papers that set the stage for the AI revolution. This week, it’s all about a way to augment and enhance your LLM with up to date, context relevant data without needing to go through pre-training all over again.
Title: Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Knowledge-Intensive NLP Tasks (Lewis, et. al. 2020)
Patrick Lewis, Staff Data Scientist, Meta
Ethan Perez, Research Scientist, Anthropic
– The authors proposed a method of augmenting language models by using non-parametric or retrieval-based memory. In essence, they introduced a fine-tuning approach where models could now access both parametric (the data the model was originally trained on) and non-parametric memory (a more up to date repository of information).
– This allowed models to revise and expand their knowledge, and the accessed knowledge can be inspected and interpretedPlain-language explanation of the core innovation
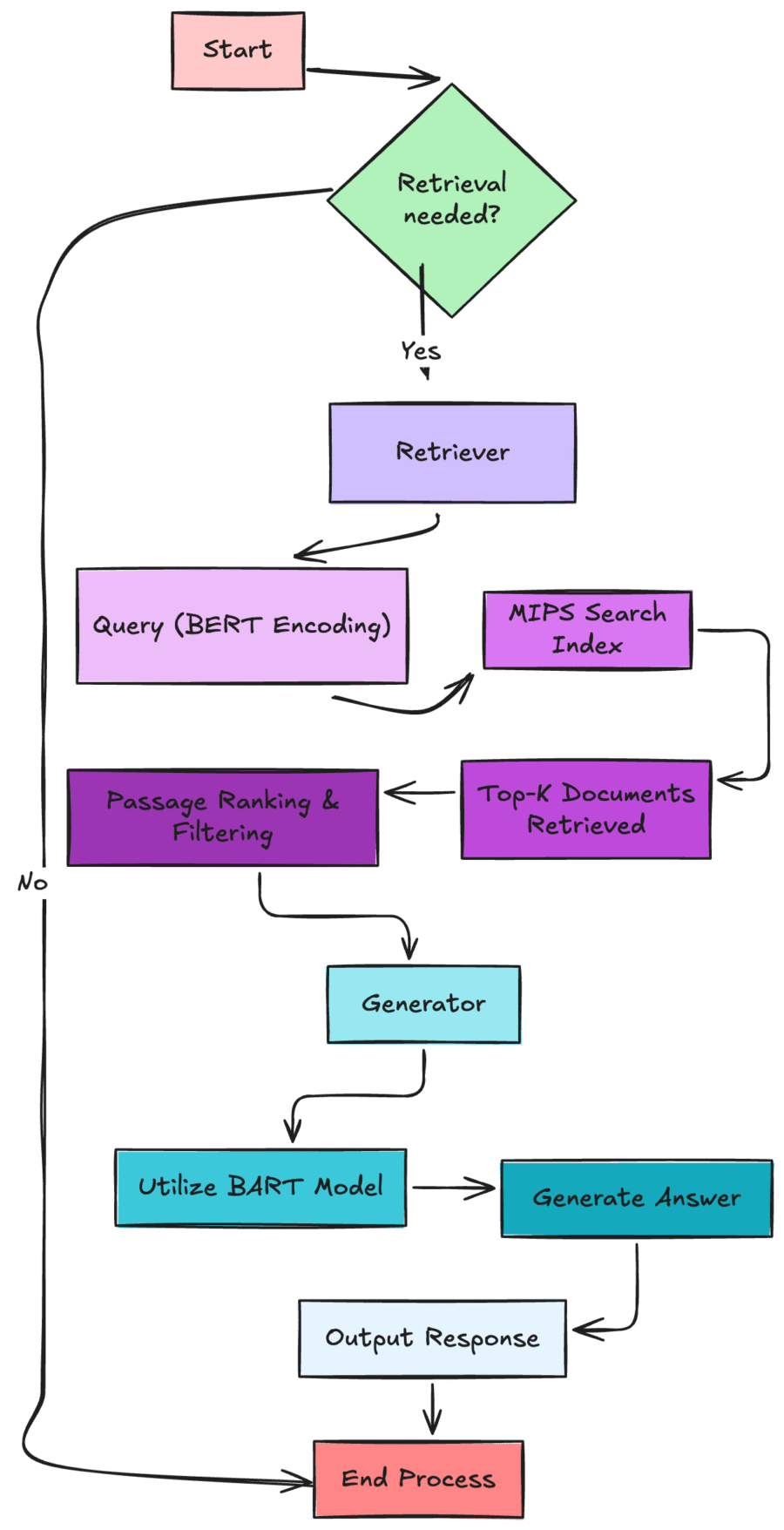
– The RAG solution comprises of two key components, the Retriever, and the Generator. The Retriever works like a librarian who’s purpose is to find the most relevant information needed to answer a question. The Generator’s job is to take the information obtained by the retriever and format it or synthesize it into a well structured answer.
– For the retriever, the authors loaded a complete dump of Wikipedia into their non-parametric memory, then they split up the data into 100-word chunks, resulting in over 21 million documents. Then they built a search index by encoding each chunk of data using a BERTBASE encoder. This embedding was trained to retrieve documents which contain answers to specific sets of trivia and natural questions.
– After performing unsupervised training, they demonstrated State of the Art (SotA)-level performance when generating specific and factually accurate responses compared to other cutting edge models.
– Critically, they also found that the document encoder could be kept fixed during training and only fine-tuning performed on the query encoder (used by the retriever) and the generator.
– This paved the way for large-scale Enterprise B2B and B2C applications for RAG.
Key Takeaways(Bulleted list)
– Open-Domain Question Answering: RAG set a new State of the Art standard by combining the generation flexibility of the “closed-book” (parametric-only) approaches and the performance of “open-book” retrieval-based approaches
– Easy to train and maintain: RAG performance scores are within 4.3% of SotA models, which are complex pipeline systems with domain-specific architectures and substantial engineering, trained using intermediate retrieval supervision, which RAG does not require.